 |
RCFP Family Planning Budget in India Infograph |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

FAMILY
PLANNING
BUDGET
IN INDIA
Though the allocation for family planning
increased by 47 per cent under the National
Health Mission, it was not enough to
compensate for a 87% and 34% decrease
in Family Welfare budget (between 2013-14
to 2015-16)".
source: Union Budget 2013-14 to 2015-16 – Expenditure Budget,
Demand No.48 (Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Department
of Health and Family Welfare); and National Health Mission (NHM)
Record of Proceedings (ROP) 2013-14 to 2015-16.
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

FAMILY PLANNING
BUDGET IN INDIA
Family Planning budget is given low priority
Cash
transfers
getting more
emphasis than
service delivery
82%
of flexi-funds for Family Planning, under National Health
Mission (NHM) {excluding the Human Resources (HR) compo-
nent} are being used for compensation to the users of sterilisa-
tion and Intra Uterine Contraceptive Devices (IUCDs) and for
incentives to staff and Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs)
77%
of the fund {excluding the Human
Resources (HR) component} is
targeted to limiting methods, most
of which is slated to be spent on
paying compensation
Proportionate Share of Family Planning in the Health Budget
n The Family Welfare budget, which
includes allocations for components of family
planning constituted only 4% of the Health
and Family Welfare budget (2014-15)
n The Family Planning (FP) budget
head was around 2% of the total
National Health Mission (NHM)
expenditure (2013-14)
Why invest in Family Planning
Every $1( 67) invested in Family Planning saves $4 ( 268) in other health and development areas,
including maternal health, immunisation, malaria, education, water and sanitation
Family Planning is an important part of the Sustainable Development Goals
(SDGs) and is closely linked to
SDG Goal 3
Ensure healthy lives
and promote well-be-
ing for all at all ages
SDG Goal 5
Achieve gender
equality and empower
all women and girls
These pertain to
Reducing
maternal
mortality
Reducing premature,
neo-natal and child
deaths
Ensuring universal access
to sexual and reproductive
health care and rights,
including family planning
information and education
1 USAID, 7 Billion and the Importance of Family Planning, USAID Deliver Project, 2011
2 NHM allocations for 2015-16 for Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand
3 NHM allocations for 2015-16 for Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
FAMILY PLANNING BUDGET IN INDIA
Decomposition by Use of Total NHM + Central Support on FP in 10 States (2015-16)
2%
IEC
11%
Incentive
4%
Training
72%
Compensation
Assam,
Bihar,
Chhattisgarh,
Jharkhand,
Madhya Pradesh
Odisha,
Rajasthan,
3%
Procure
8%
Other
Uttar Pradesh,
Uttarakhand,
Himachal
Pradesh.
Sources of Public Financing of Family Planning in India
Family Welfare
(Central Sector)
Family Planning
(under National Health Mission)
Family Welfare
(State Budget)
Free distribution of contraceptives
Procurement (of contraceptives,
sub-centre kits, etc.)
Infrastructure maintenance (cost of
sub-centres and ANMs)
Social marketing projects
FP linked health insurance
Sterilisation and IUD services in
camp mode
Accreditation of private facilities for
providing FP services
Training
IEC materials
Procurement of FP consumables
Central support for FP
State support for salaries,
mobility and routine expenses
(no capital expenditures)
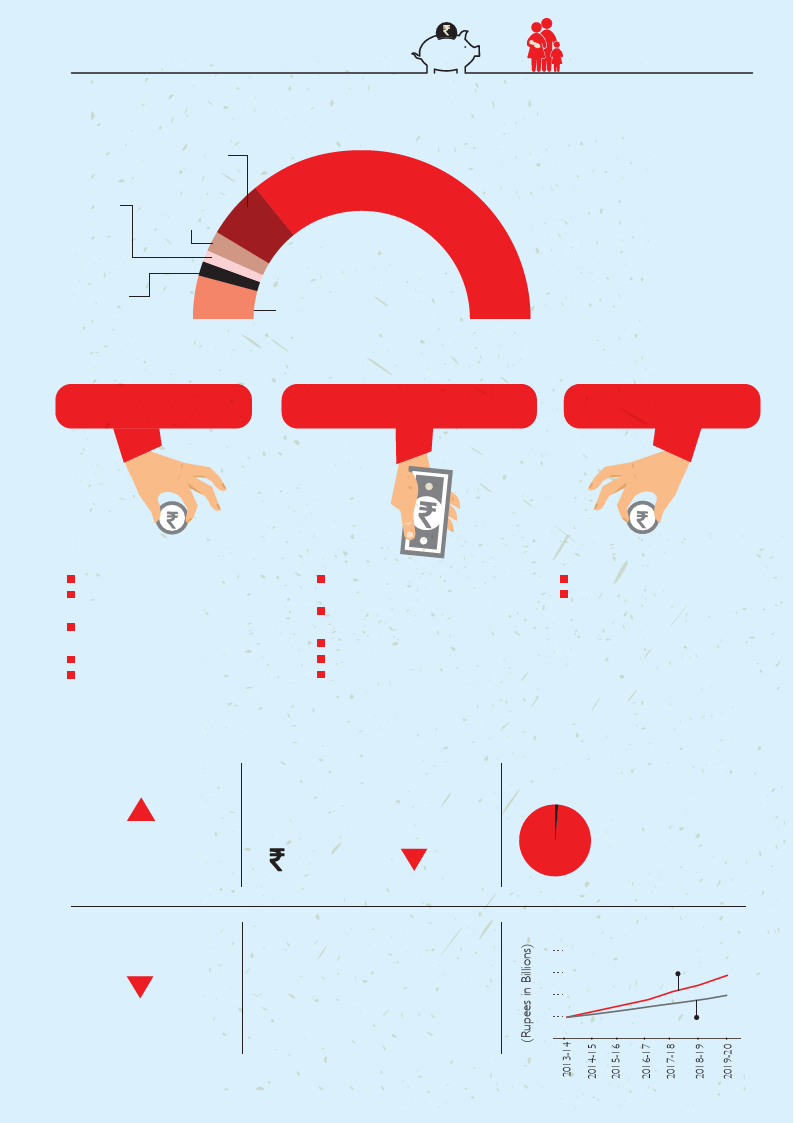
Family Planning Budget Trends (national level)
Over 2013-14 and
2015-16,
47%
increase in the NHM
allocation for FP (under the
Reproductive and Child
Health (RCH) Flexi-pool
route of NHM)
Central Sector
resources have
been reduced by
54%
between 2013-14
and 2015-16
Current trend of increase in FP
budget indicates that it would fall
short of the resources necessary to
meet the requirement of additional
FP users by almost
1,500cr
(US $231 million)
The declining trend
from 2011-12 raises serious concerns
about the sustainability of FP services
to meet rising future needs, as the
contraceptives and IEC materials are
obtained from this budget
Just
1.45%
of the total family
planning expendi-
ture under NHM
is on spacing
methods,
reflecting a lack
of much needed
attention
FP Budget - Current Trend
30 FP Budget required to cover
the expected increase in mCPR
25
20
15
Current trend of FP Budget
10
4 PFI study on resource requirement for India’s FP2020 commitments
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
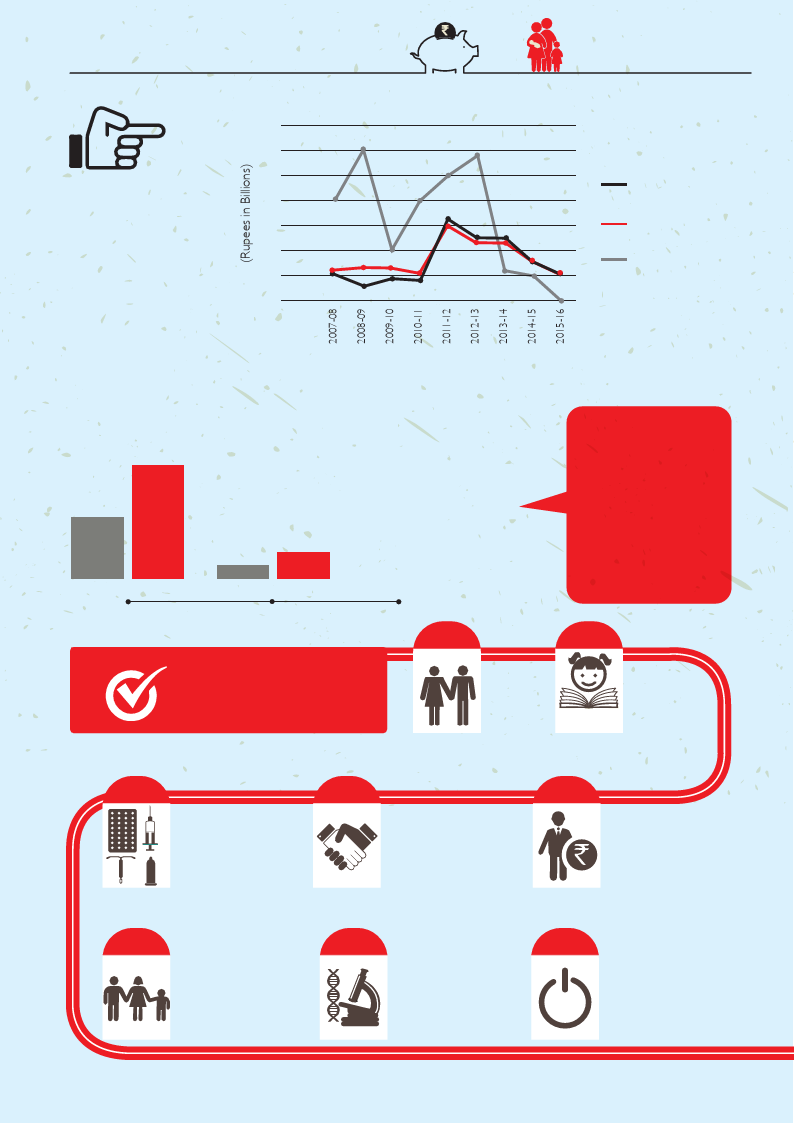
FAMILY PLANNING BUDGET IN INDIA
3.5
3
2.5
Trend in Actual
2
Allocation
through Central
1.5
Sector Budget
1
for FP
0.5
0
Social Marketing of
contraceptive
Free Distribution of
Contraceptive
Procurement of
Supplies & Materials
Family Planning Budget Trends (state level)
Approved allocation for Family Planning (under NHM)
An increase of
84%
in just two
years
An increase of
88%
in just two years
115cr 212cr
2013-14
2015-16
27cr 51cr
2013-14 2015-16
Bihar, on the
other hand,
showed a
comparatively
sluggish
growth of
44%
in two years
Uttar Pradesh
Odisha
Bihar
States’ capacity
to generate
additional funds
for FP look grim,
as there is an
increasingly
tighter fiscal
space.
Priorities and
Way Forward
Focus
on
young
couples
Tackle the
population
momentum
Shift focus from
permanent
methods and
promote spacing
methods
Encourage the
involvement of
private players
Budget for
training service
providers and
task shifting
Promote Male
involvement in
family planning
Research
in newer
methods
Digitisation
of supply
chain
management
CONTACT US : Population Foundation of India, B-28, Qutab Institutional Area, new Delhi- 110016 | Tel: +91 43894100





